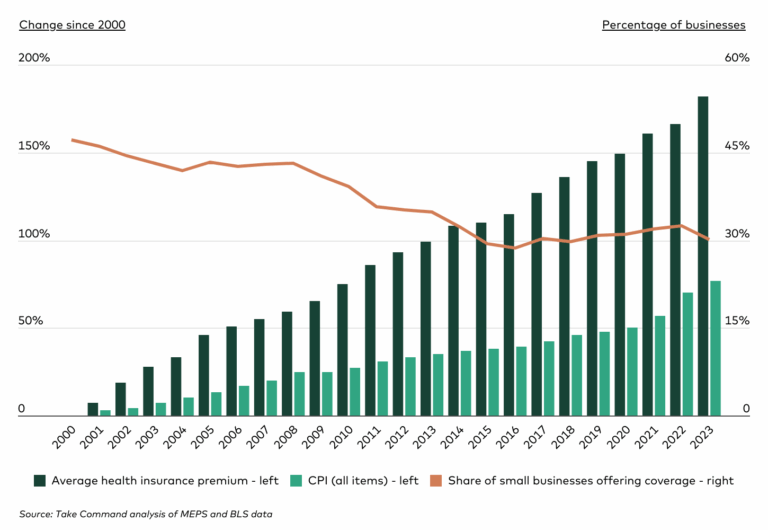
The Shrinking Landscape of Small Business Health Insurance
Rising healthcare costs have significantly impacted small businesses across the United States, particularly those with fewer than 50 employees. The proportion of these businesses offering health insurance has declined substantially over the past two decades, dropping from 47.2% in 2000 to 30.1% in 2023. This decrease coincides with a sharp rise in the cost of employer-sponsored insurance, with average annual premiums for small businesses increasing by 182% between 2000 and 2023, far outpacing the 77% rise in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) during the same period.
Several factors have contributed to this trend. The Great Recession of 2008-2009 financially strained small firms, leading many to cut back on benefits. The implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010 also played a role, as businesses with fewer than 50 full-time employees were exempt from the employer mandate. Some firms subsequently dropped their group health insurance plans, opting instead to allow employees to purchase subsidized insurance through individual marketplaces.
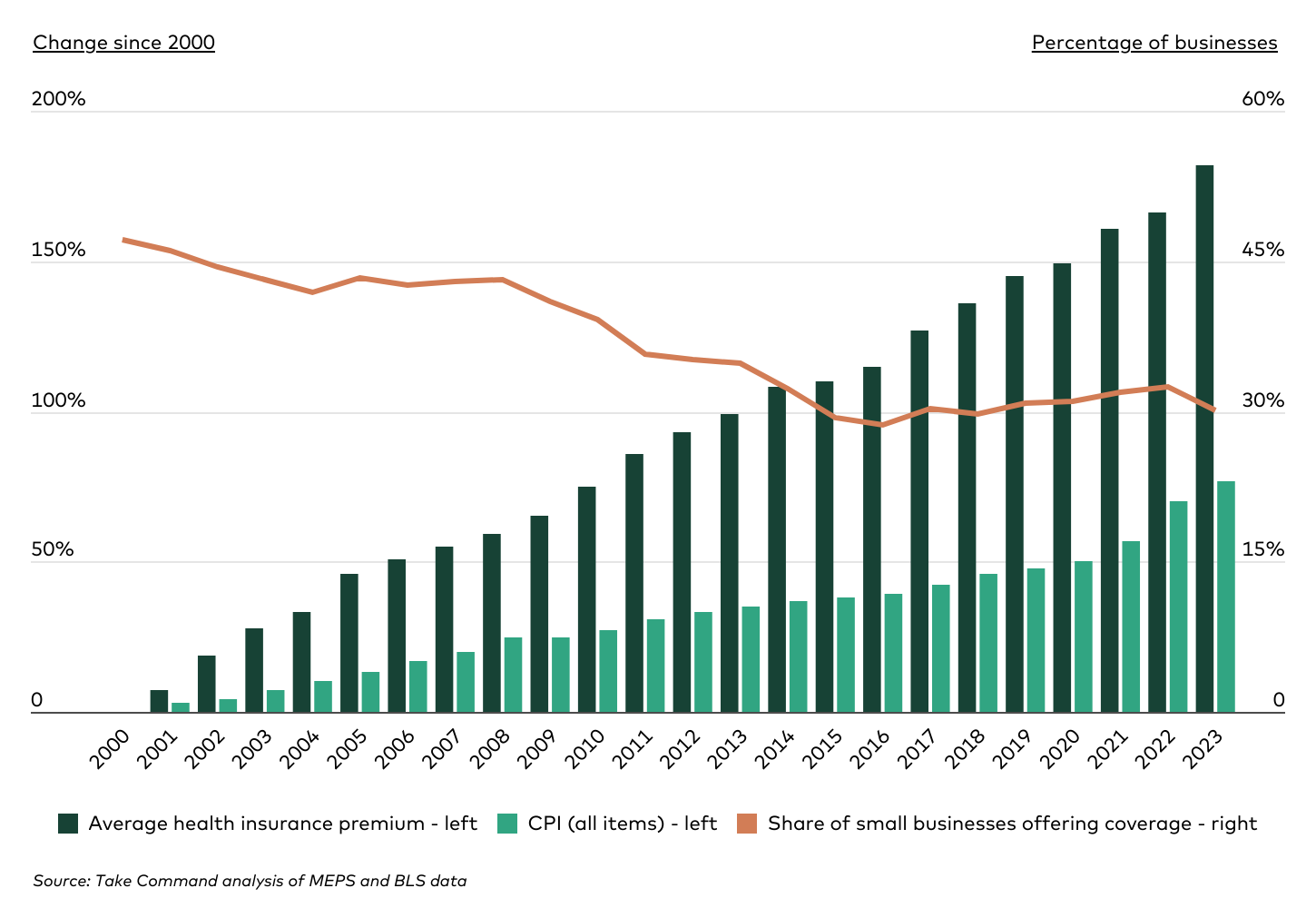
Industry-Specific Declines in Health Coverage
The decline in health insurance coverage among small businesses has been observed across various industries, with some experiencing more significant drops than others. The wholesale trade sector saw a 17.6 percentage point decrease in coverage between 2009 and 2023, while mining and manufacturing firms dropped by 13.3 percentage points, and professional services fell by 13.2 percentage points.
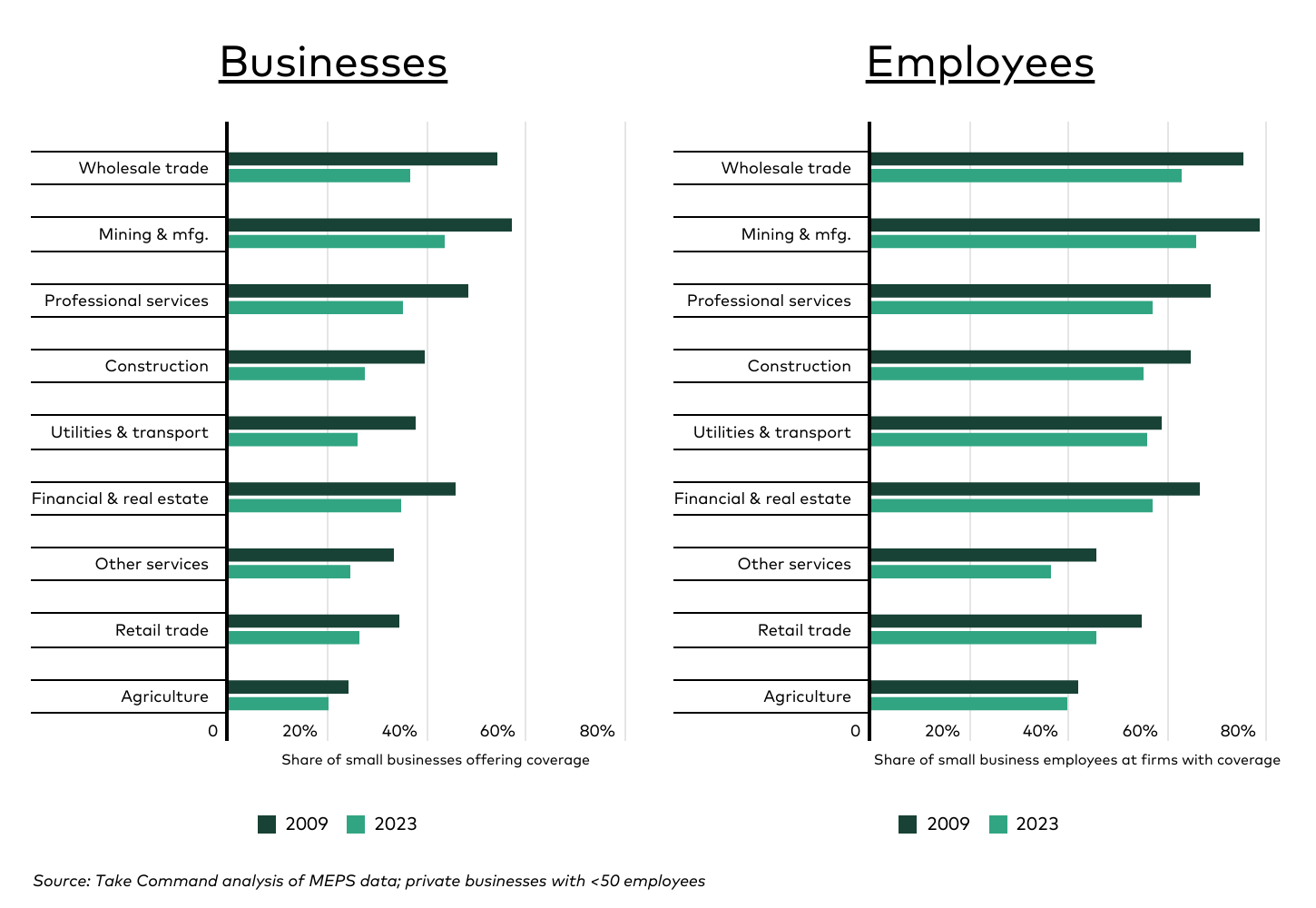
Regional Variations in Small Business Health Coverage
The decline in small business health coverage has not been uniform across the United States. Northeastern states have experienced some of the steepest losses, with Connecticut leading the nation in decline at 24.6 percentage points between 2009 and 2023. In contrast, states like Hawaii continue to maintain high levels of coverage due to state-specific regulations.
Emerging Trends in Small Business Health Benefits
In response to rising costs and changing regulations, many small businesses are exploring alternative approaches to providing health benefits. Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) have gained popularity as a flexible and cost-effective option. The adoption of HRAs nearly tripled between 2020 and 2024, with over 80% of employers offering them to provide benefits for the first time.
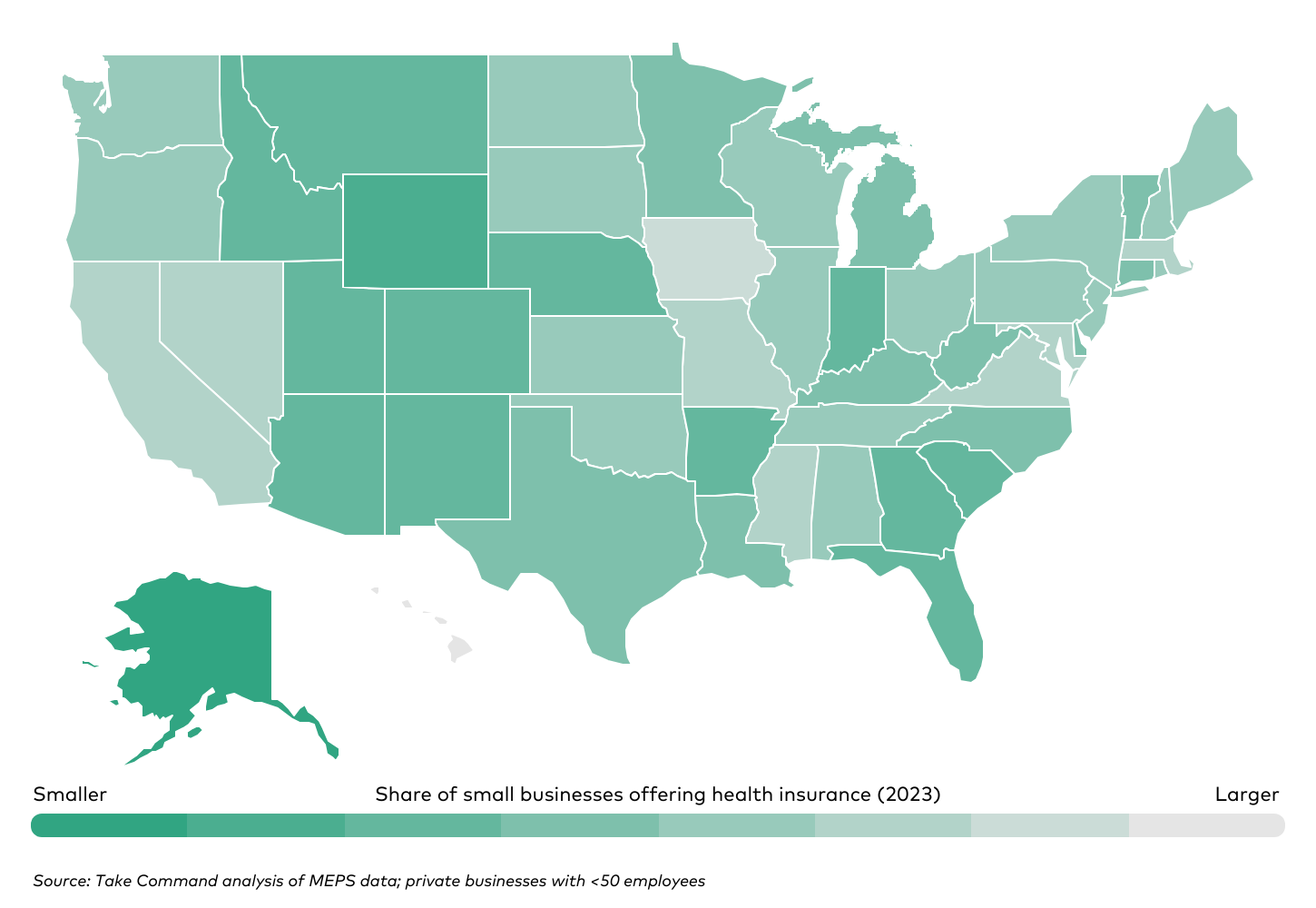
State-by-State Comparison of Small Business Health Coverage
There remains significant variation in small business health coverage across different states. Hawaii stands out as a leader, with 71.8% of small businesses providing coverage, thanks to the Hawaii Prepaid Health Care Act. Conversely, states like Wyoming and Alaska have some of the lowest coverage rates, with fewer than one in five small firms offering health insurance.
The decline in traditional employer-sponsored health insurance among small businesses does not necessarily translate to reduced access to healthcare. Many workers are turning to alternative coverage options, contributing to a historically low national uninsured rate. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the sustainability of coverage for employees at small firms will likely depend on strengthening individual markets and expanding flexible benefits models.