The Insurance Industry’s Inflection Point
The insurance industry is at a critical juncture, having weathered the Covid-19 pandemic but now facing numerous challenges. Recent rate-driven growth is unsustainable due to unaffordable property premiums and declining relevance of life insurance. The rise in natural disasters, cyberattacks, and new transportation technologies demands innovative risk models with a stronger focus on prevention.
Challenges and Opportunities
Insurers face significant protection gaps, with only one-quarter to one-third of natural disaster damages covered by insurance projected by 2030, and less than half of mortality risks covered. To bridge these gaps, insurers must address affordability in property and casualty (P&C) insurance and regain relevance in life insurance through better customer access and engagement.
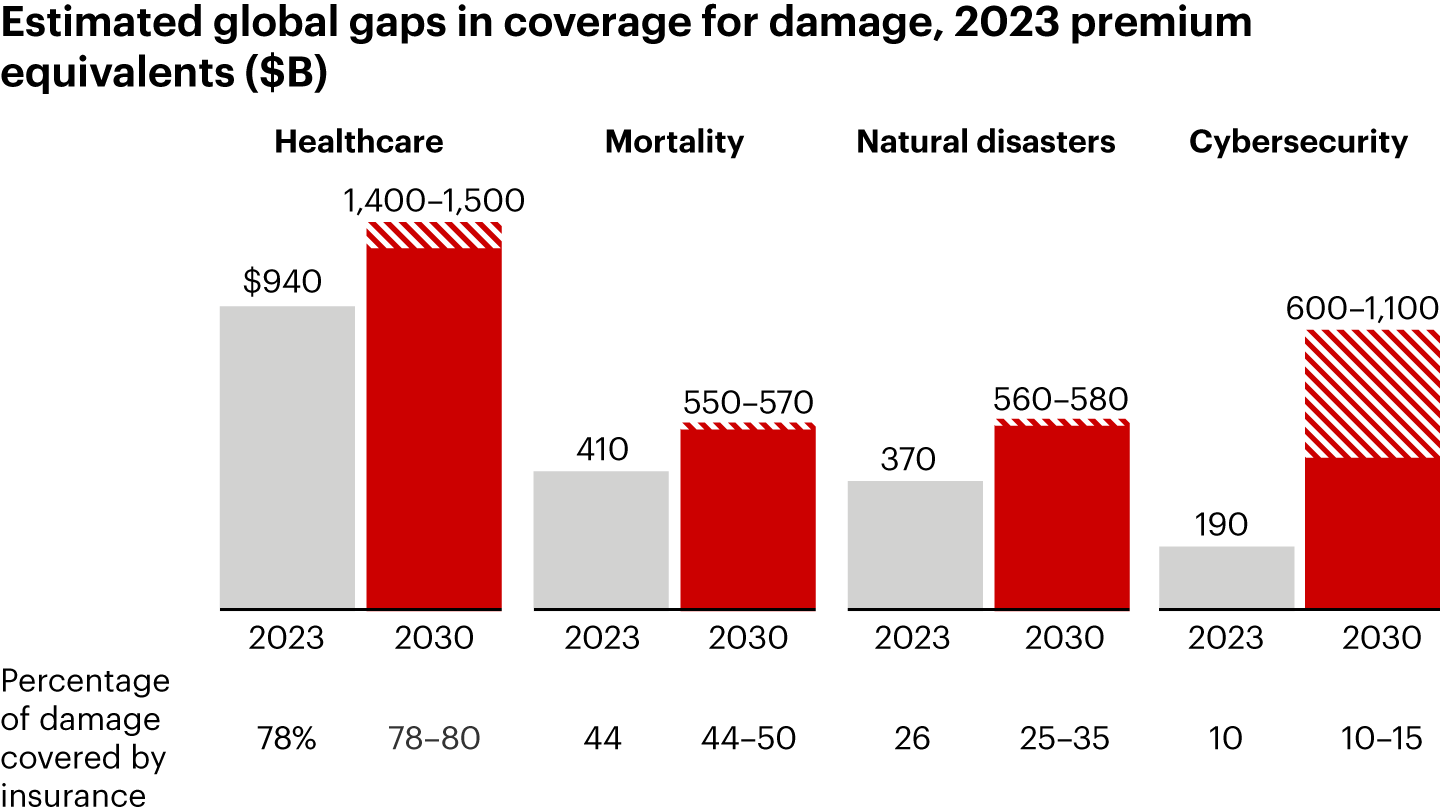
Prevention services offer a significant opportunity for insurers to add value by helping customers mitigate risks, reducing claims, and enhancing policyholder relationships. Six critical themes are emerging for insurers to consider:
- Shifting Customer Circumstances: Economic constraints are reshaping consumer behavior, forcing insurers to reconsider strategies, particularly in the face of rising property premiums and changing life expectancy.
- Emerging Risks: Climate-related disasters, cyberattacks, and technological advances in transportation are reshaping risk landscapes, requiring new products and prevention strategies.
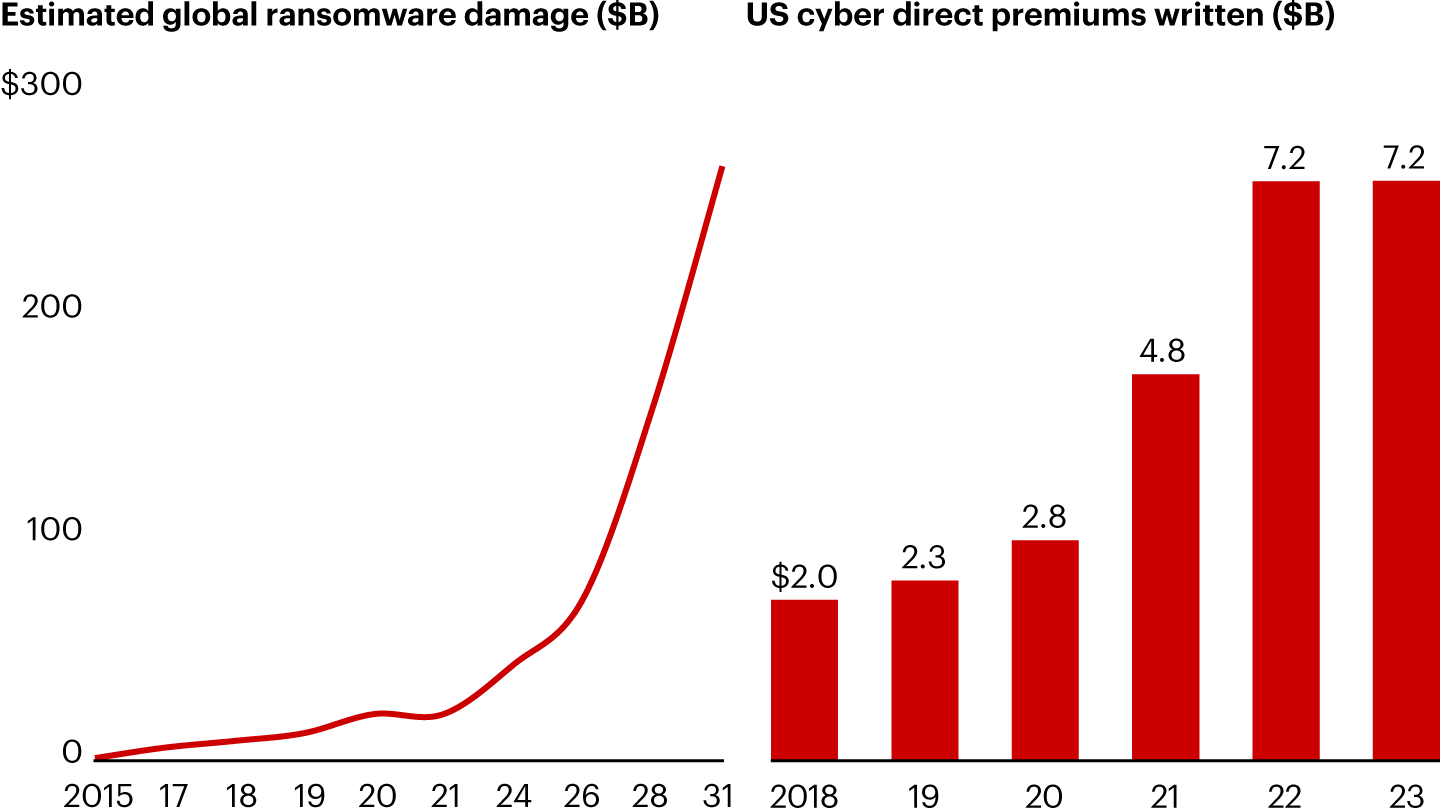
- Customer Engagement: Changing consumer behavior and digital channels are reshaping how insurance is researched and purchased, with embedded insurance models gaining traction.
- Unstructured Data and AI: The proliferation of unstructured data and AI is revolutionizing the industry, offering opportunities for enhanced affordability, access, and operational efficiency.
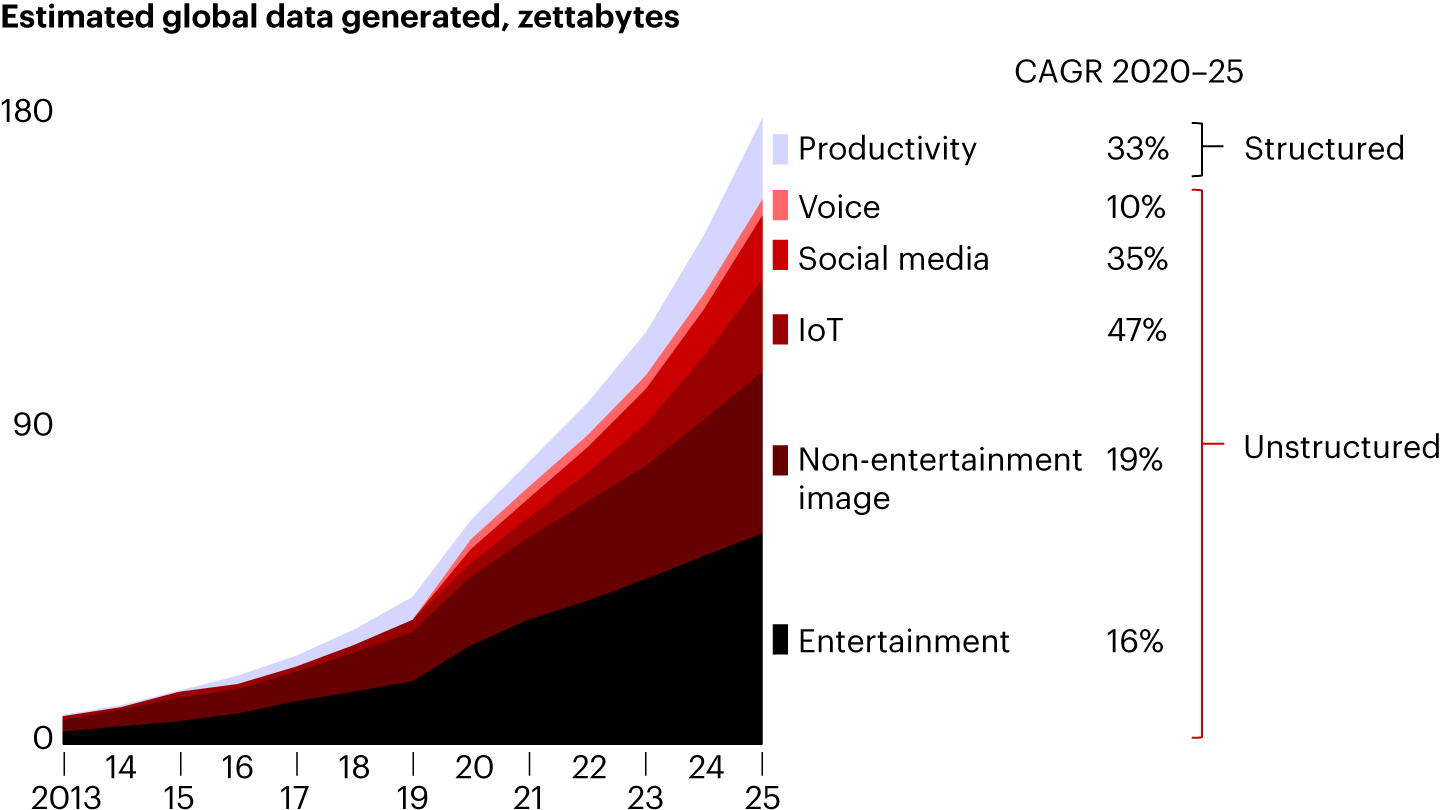
- Retirement Cliff: The industry faces workforce challenges as seasoned professionals retire, requiring insurers to emphasize technology literacy and critical thinking.
- Alternative Capital: Insurers are increasingly using alternative instruments to improve risk-adjusted returns and capacity.
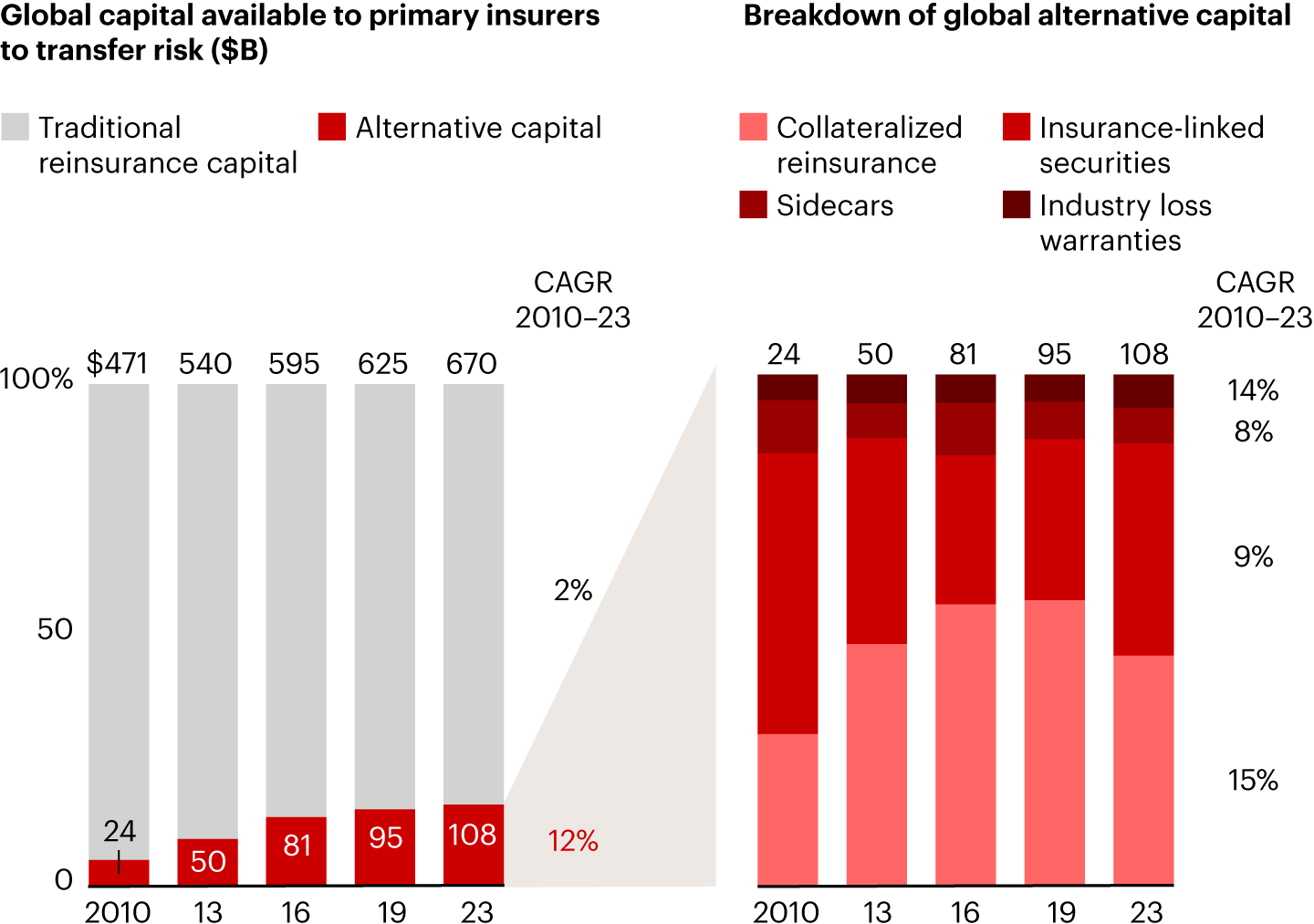
To succeed, insurers must modernize data systems, transform workforces, and renovate product portfolios. By doing so, they can achieve sustainable growth while making the world safer amid rising risks.

