Aligning Insurance with Data: The Rise of AI in Underwriting
Data is the lifeblood of the modern world, and the insurance industry is no exception. Traditionally, insurance underwriting relied on manual assessments, but advanced analytical techniques, including statistics and generalized linear models, have become commonplace. Now, Artificial Intelligence (AI) in underwriting is emerging as a game-changer, promising to revolutionize how risk is assessed and policies are priced.
The Need for AI in Underwriting
Manual underwriting, while offering a personalized touch, presents several challenges that AI can effectively address:
- Lengthy Process: Manual underwriting is time-consuming and often less accurate and slower than AI-driven approaches.
- Increased Complexity: The complex paperwork and potential for errors can frustrate and deter the customer.
- Decreased Efficiency: Manually assessing risk variables is resource-intensive, impacting organizational productivity.
- Inefficient Pricing: Manual underwriting is prone to errors when determining the level of risk.
Forward-thinking insurance companies are already implementing AI in underwriting to improve efficiency and accuracy, and to solve the pain points of manual underwriting.
The Benefits of AI in Underwriting
AI offers numerous advantages for insurance companies:
- Minimized Possibility of Human Error: AI can process vast datasets in various formats, reducing the chance of errors and providing more consistent evaluations. This enables human underwriters to make more informed choices based on the data, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Improved Risk Understanding: AI broadens access to relevant data sources and enhances risk assessments, as well as introducing predictive analytics models and big data, and machine learning. These solutions help reduce time-consuming due diligence procedures.
- Cyber Threat Combat: AI-powered fraud detection systems help anticipate and mitigate emerging cybersecurity threats, which are crucial in today’s digital landscape.
- Improved Customer Loyalty: AI streamlines the sales process and fosters customer loyalty with customized plans. In addition, it frees up underwriters for for more valuable interactions.
- New Business Acquisition Opportunities: AI-driven systems facilitate cross-platform visibility and generate insights. Using NLP-powered chatbots, underwriters can engage clients with customized plans before applications are submitted, gaining a comprehensive view of the customer’s needs.
- Fairer Pricing: Automated underwriting allows for more accurate risk profiles.
- Increased Profitability:AI helps underwriters produce lower loss ratios and optimize the total resources used which results in increased profitability for the companies.
Roadmap to Integrate AI in Insurance Underwriting
Implementing AI in underwriting involves a structured approach:
- Regulate and digitize the underwriting process: Conduct process audits, digitize paper-based processes and establish performance standards.
- Automate manual and repetitive activities with AI: AI supports data collection and presentation, while human workers improve underwriting judgments based on these inputs.
- Apply AI in more evolved processes: AI leads the underwriting process, making judgments based on contextual and factual understanding, with human underwriters acting as supervisors.
AI in Underwriting Automation Journey
Commercial insurers are moving from manual workflows to automating various aspects of underwriting. The journey comprises three stages:
- Prefill: AI uses various data sources to auto-populate application data for minor commercial risks, providing classification suggestions. Human underwriters then evaluate this information.
- Selective Automation: Select insurance sectors for automated underwriting, comparing prefilled data to standards and automatically applying credits or debits. A quote can be generated automatically.
- Full-blown Automation: Expand automation to other business segments to automate operations and gain greater efficiency.
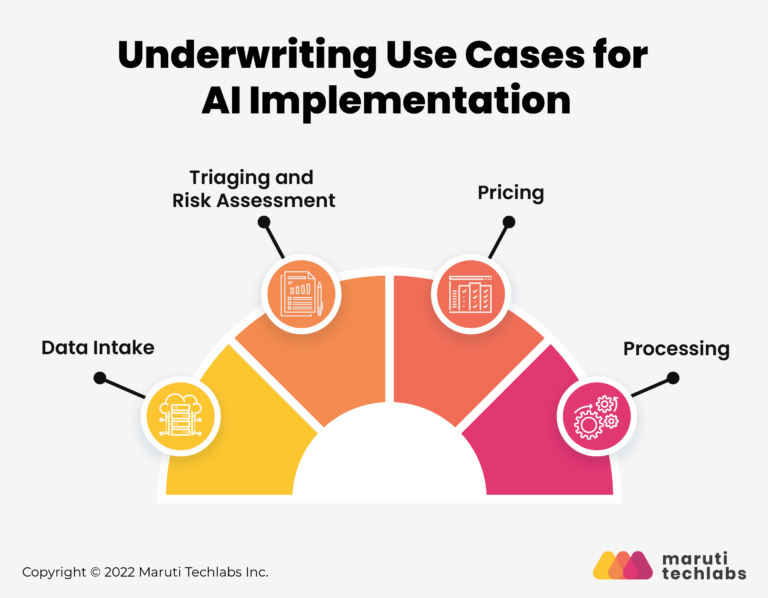
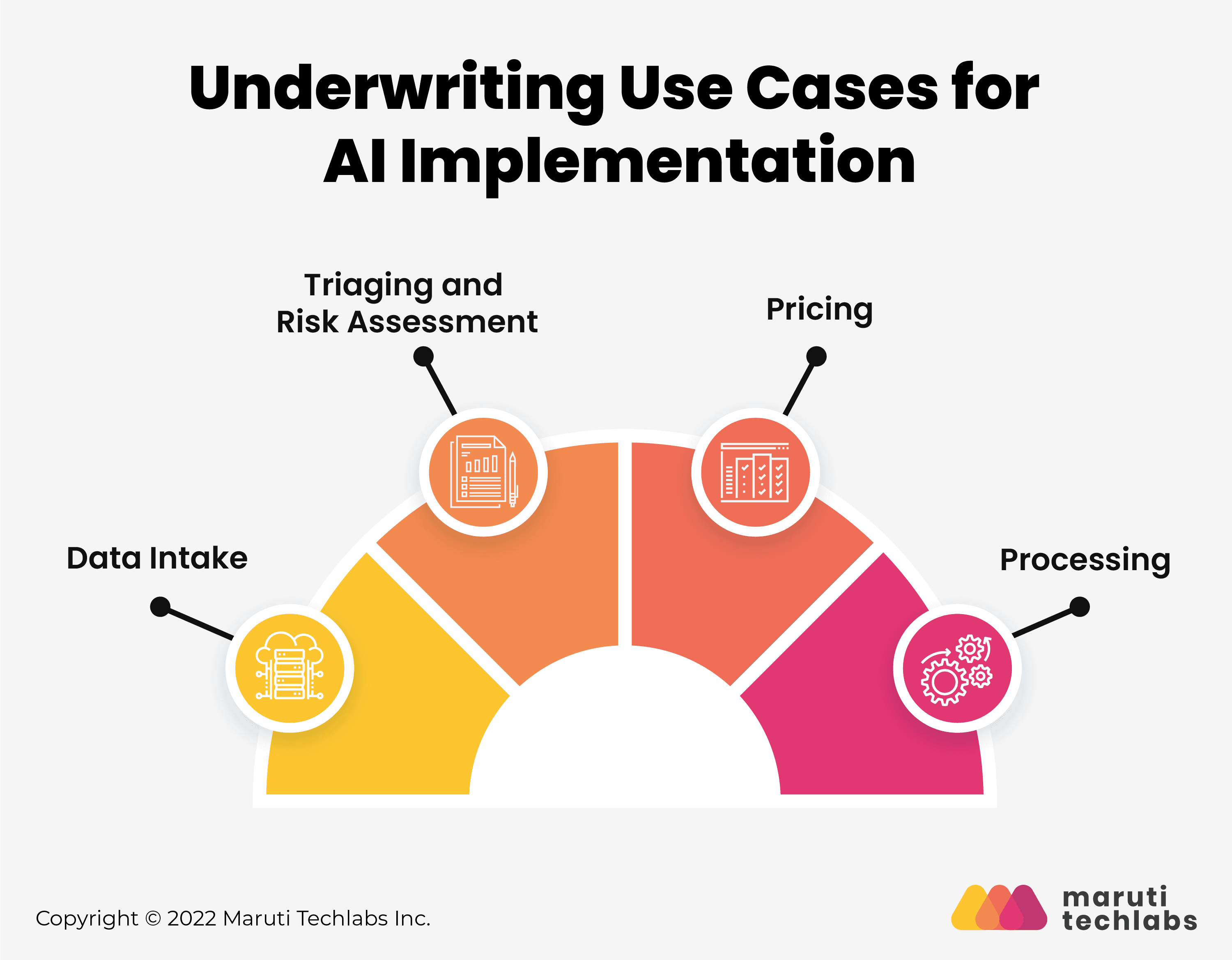
AI for Underwriting Modernization – Use Cases &
Applications
- Data Intake: AI automates data collection, extraction, and processing from multiple sources, increasing efficiency and accuracy using optical character recognition and NLP.
- Triaging and Risk Assessment: Intelligent automation uses rules and AI to categorize and triage data, assisting underwriters in risk assessments by handling lower-value policy submissions and coaching the AI.
- Pricing: AI and machine learning construct pricing models based on risk variables and client attributes, helping to determine the policy pricing that will provide the highest return.
- Processing: RPA and intelligent automation handle administrative tasks, making it possible to extract data from various platforms and control overall policy underwriting workflows.

Underwriting Modernization Strategy – 4 Steps
To successfully modernize, businesses must restructure and use agile principles:
- Adopt systems approach: Understand interactions within the underwriting process and streamline submission and requirements gathering, prioritizing standards for risk assessment.
- Break down silos: Foster cross-departmental coordination and introduce new roles such as data science to achieve organizational goals.
- Bring changes from the highest level: Secure buy-in from senior leaders to maintain momentum and conviction, and communicate distinct goals.
- Fast-track the pace: Deliver bite-sized features frequently and adapt to feedback loops, shortening product development cycles.
Conclusion
AI in underwriting is no longer a futuristic concept but a necessity for insurance companies looking to remain competitive. Embracing AI enables insurers to generate value from data, attract top talent, and provide better customer experiences, all leading to a positive feedback loop. Companies reluctant to integrate AI face the risk of falling behind in the industry. Prioritizing underwriting modernization is a strategic imperative. To succeed, insurers must move quickly and make sure that they have the right tools and practices in place.